They are most common at divergent boundaries.
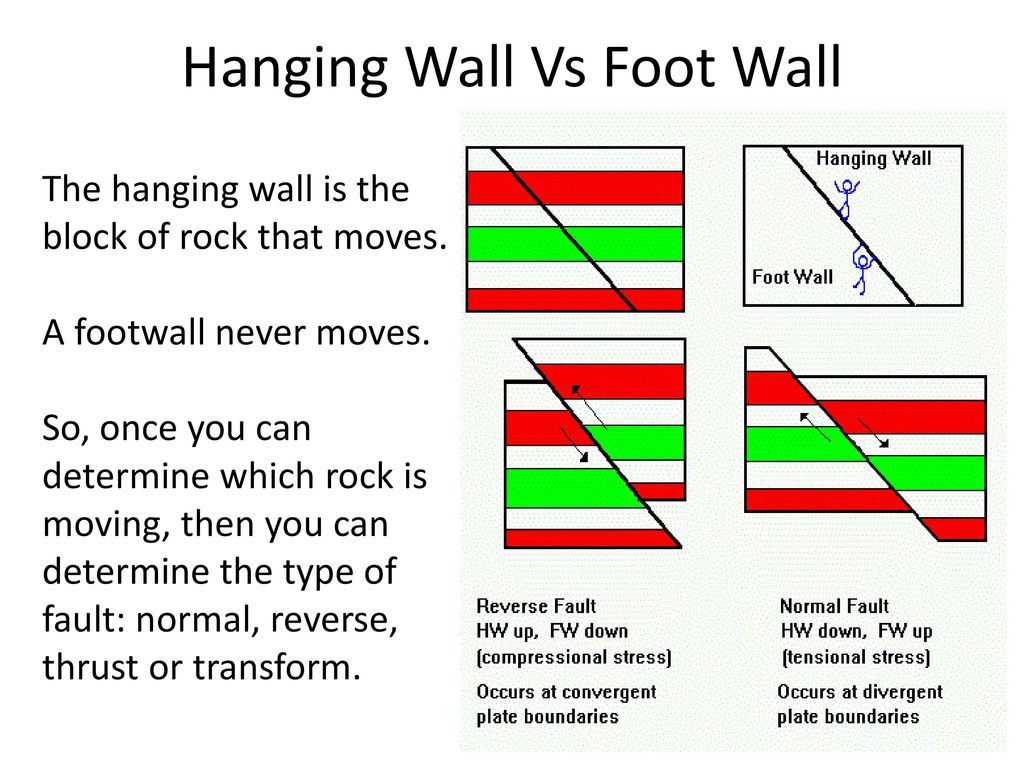
Relative motion of plates and hanging wall and foot wall.
A dip slip fault in which the block above the fault has moved downward relative to the block below.
Up and down motion so the footwall moves up and the hanging wall moves down.
Hanging wall moves down relative to foot wall.
A downthrown block between two normal faults dipping towards each other is a graben.
Faults are made up of a footwall and hanging wall.
Every fault tilted from the vertical has a hanging wall and footwall.
Left lateral or sinistral.
In a strike slip fault a the hanging wall moves down relative to the footwall b the hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall at the angle of 30 degrees or less c the hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall at an angle of 45 degrees or more d the fault blocks move horizontally in opposite directions.
Occurs when the hanging wall moves down relative to the foot wall reverse fault.
Then you determine the relative motion between the hanging wall and footwall.
The type of fault in which the relative motion of the hanging wall with respect to the foot wall is down is called a.
These faults place younger and or lower grade rocks on top of older and or higher grade rocks.
Up and down motion again but hanging wall moves up footwall moves down.
This type of faulting occurs in response to extension.
We classify faults by how the two rocky blocks on either side of a fault move relative to each other.
Splinters of the oceanic plate that are scraped off the upper part of a descending oceanic plate and welded onto the forward edge of the overriding continental plate is called.
A dip slip fault in which the upper block above the fault plane moves up and over the.
2 reverse or thrust fault.
Visualise the footwall on the left and the hanging wall on the right just as an example.
Low angle normal faults with regional tectonic significance may be designated detachment faults.
Normal faults form when the hanging wall drops down in relation to the footwall.
In a normal fault the hanging wall moves downward relative to the footwall.
To correctly identify a fault you must first figure out which block is the footwall and which is the hanging wall.
Extensional forces those that pull the plates apart and gravity are the forces that create normal faults.
All at once crack the rock breaks and the two rocky blocks move in opposite directions along a more or less planar fracture surface called a fault.
All the stress and strain produced by moving plates builds up in the earth s rocky crust until it simply can t take it any more.
Right lateral or dextral.